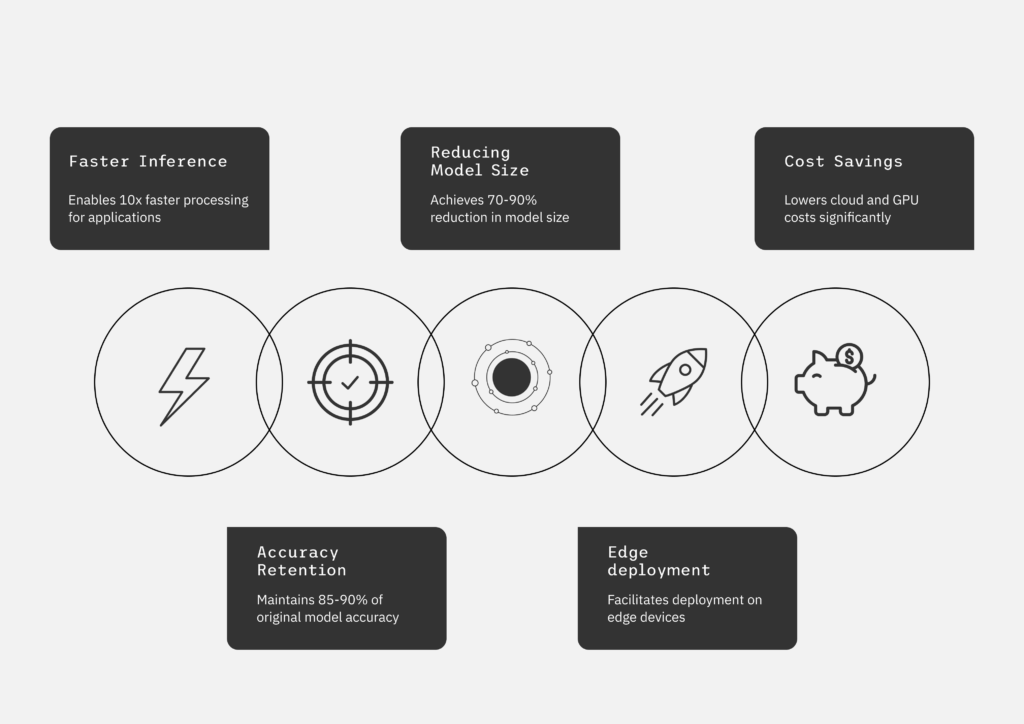
In the rush to implement AI across organizational operations, one must strike a balance between adaptability and accuracy. Should you rely on retrieval-based intelligence to maintain agility, or should you hardwire experience into the model to ensure precision?
This is a strategic decision, and making the right call at the right time can determine the success of everything from automated policy interpretation to conversational AI. Both offer paths to smarter AI; however, they serve different needs, and selecting the wrong one can be the difference between insight and illusion.
RAG: Fast, Flexible, and Context-Aware
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is where most organizations begin their journey. Instead of retraining an LLM, RAG enhances its responses by pulling real-time context from a vector database. Here’s how it works:
- Vector Encoding: Your documents or knowledge base are embedded into a vector store.
- Prompt Engineering: At inference time, the user’s query triggers a semantic search.
- Dynamic Injection: Relevant documents are retrieved and included in the prompt.
- LLM Response: The model uses this injected context to generate a grounded, informed response.
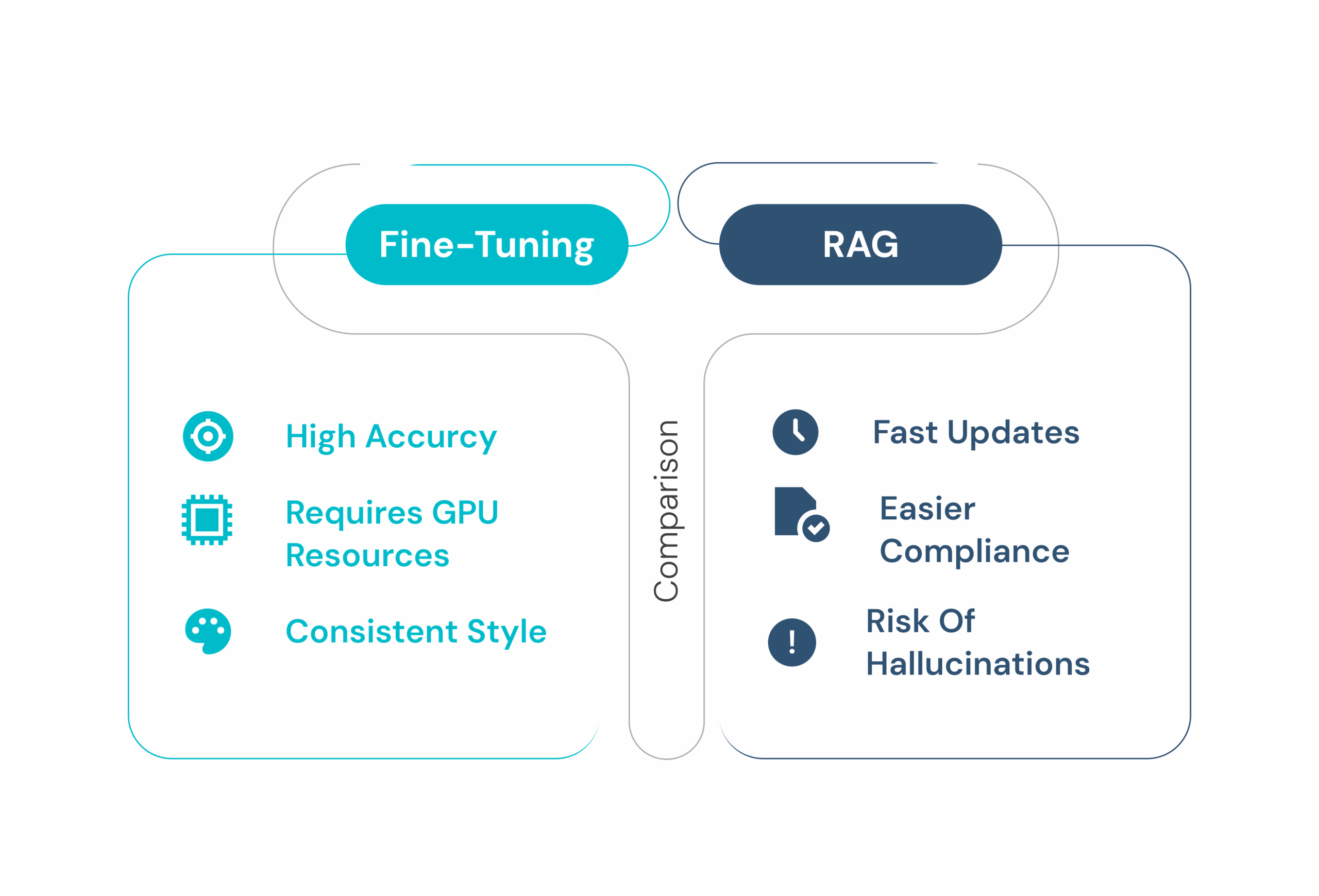
This process is compute-efficient, versionless, and ideal when knowledge is fluid or frequently updated, such as government policies, IoT feeds, or legal frameworks.
Where Does RAG End?
While RAG excels at injecting facts, it has limitations:
- It can’t teach the model how to reason.
- It doesn’t enforce stylistic consistency.
- And when retrieval fails, hallucinations creep in.
That’s your cue: when structure, tone, or deterministic behavior become priorities or when retrieved content isn’t enough to answer correctly, you transition to fine-tuning.
Enter Fine-Tuning: Precision with Permanence
Fine-tuning involves retraining the base model on your domain-specific data, embedding domain-specific language, decision logic, and formatting directly into its parameters.
This is essential when:
- You want consistent behavioral patterns (e.g., legal summaries, medical reports).
- You need high accuracy where the retrieval is partially optimal or completely absent.
- Your workflows involve fixed taxonomies or templates.
- Hallucination pt.
Fine-tuning embeds knowledge deep into the model for deterministic output.
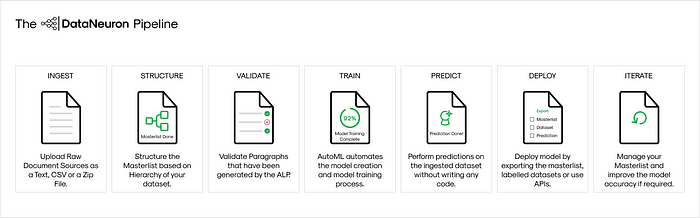
Build Both With DataNeuron Without Building Infrastructure
Unlike fragmented ML stacks, DataNeuron lets you orchestrate RAG and fine-tuning in a single interface. Most platforms force teams to juggle disconnected tools just to get a basic RAG or fine-tuning pipeline running. DataNeuron changes that.
- Unified no-code interface to design, chain, and orchestrate both RAG and fine-tuning workflows without DevOps dependency
- DSEAL powered Dataset Curation to automatically generate high-quality, diverse datasets, structured and ready for fine-tuning with minimal manual prep
- Built-in prompt design tools to help structure and adapt inputs for both generation and retrieval use cases
- Robust evaluation system that supports multi-layered, continuous testing spanning BLEU/ROUGE scoring, hallucination tracking, and relevance validation, ensuring quality improves over time
- Versioned model tracking and performance comparison across iterations, helping teams refine workflows based on clear, measurable outcomes
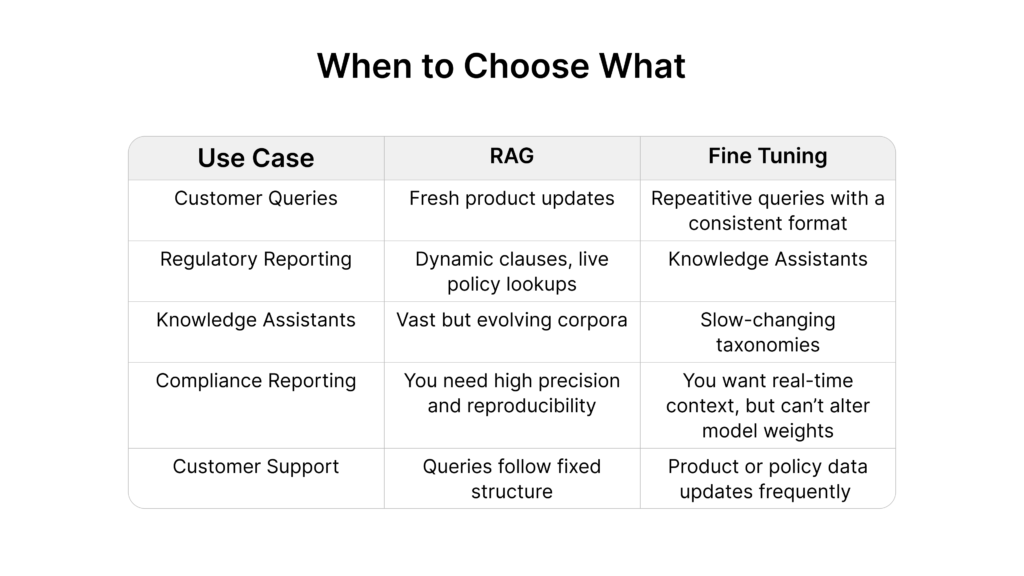
Use DataNeuron to monitor and iterate across both workflows.
- Fine-tune the LLM for tone, structure, and in-domain reasoning.
- Layer in RAG to supply the most recent facts or data points.
This hybrid pattern ensures that your AI communicates reliably and stays up to date.
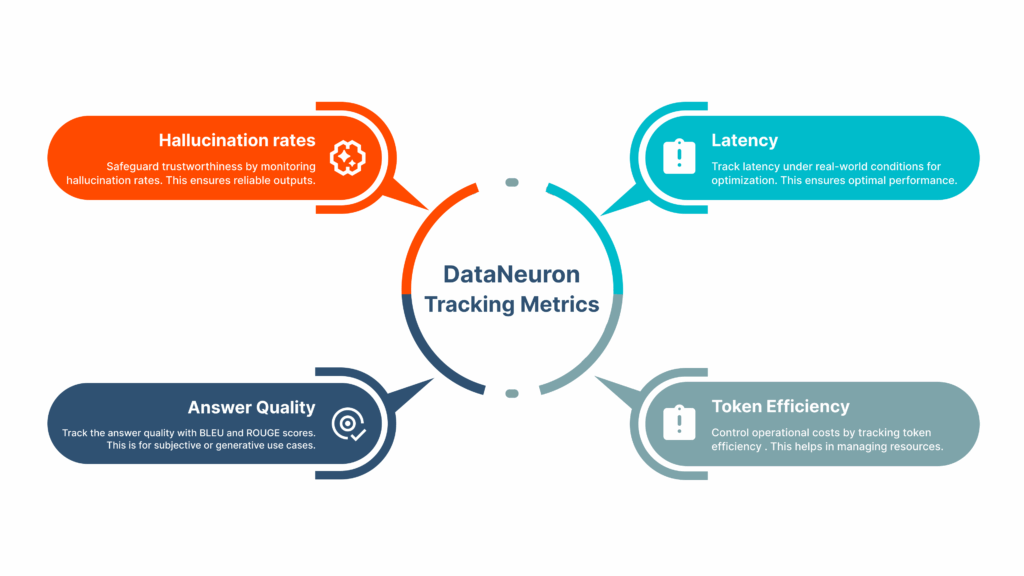
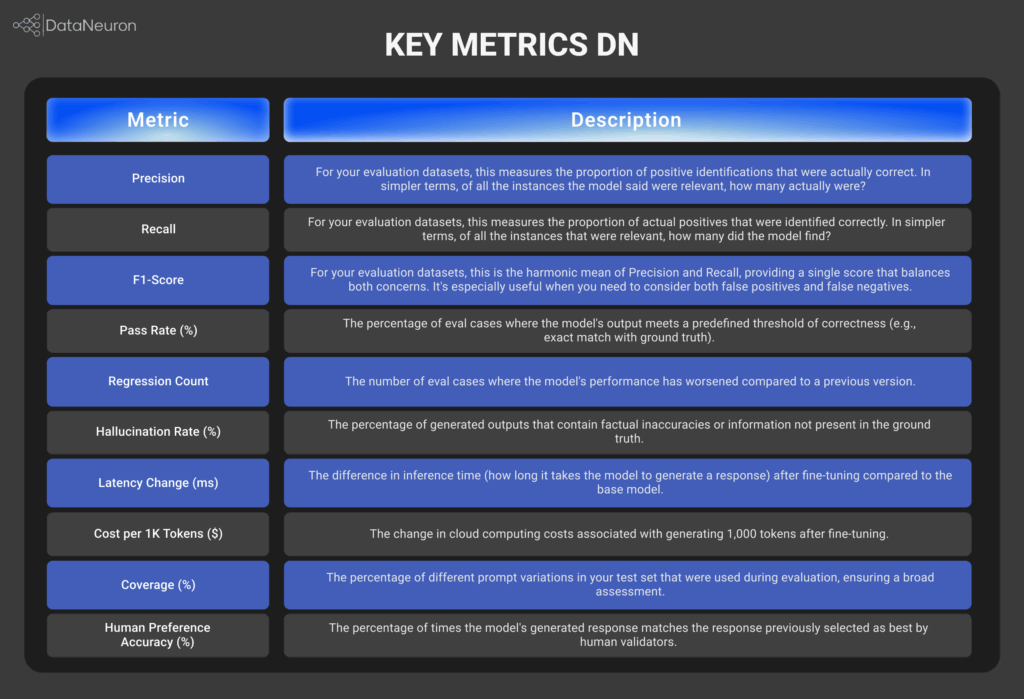
These metrics help ensure both your fine-tuned and RAG-based pipelines stay grounded, efficient, and aligned with real-world expectations.
Start Smart with DataNeuron
- A customer support team used fine-tuning on 10,000 Q&A pairs and cut error rates by 40%.
- A public sector client layered RAG into live deployments across 50+ policies, with no retraining needed.
Both teams used the same platform. One interface. Multiple workflows. Wherever you are in your AI journey, DataNeuron gets you moving quickly.